Fatigue failure in a camshaft normally starts at stress concentrations such as fillets, oil holes, keyways, or notches, and is caused by repeated bending and torsional loads during engine operation. 1. Identify Critical Locations Use experience and inspection to locate: ●Cam lobe fillets ●Bearing shoulders ●Oil holes ●Keyways and grooves These areas experience the highest stress and are typical crack initiation sites. 2. Determine Operating Loads Calculate cyclic loads from: ●Valve spring forces ●Torsional vibration from crankshaft ●Inertial loads at operating RPM This produces a combined bending–torsion stress cycle. 3. Stress Analysis (FEA) Perform finite element analysis to obtain: ●Local stress distribution ●Maximum principal stress at critical locations ●Stress gradients near notches 4. Convert Stress to Fatigue Parameter Traditional Method: Use the local stress and apply: ●S–N curve of camshaft material ●Notch sensitivity corrections ●Mean stress correction (Goodman / Gerber / Soderberg) This method works reasonably for smooth geometries but becomes unreliable near sharp or complex notches. Advanced Method: Crack Modelling Instead of using stress alone, the notch is treated as an equivalent crack: 1.Extract the stress field near the notch from FEA. 2.Convert it into an equivalent stress intensity factor (K). 3.Compare cyclic K to the fatigue crack growth threshold (ΔKₜₕ). 4.If ΔK > ΔKₜₕ → fatigue crack initiates and failure is predicted. This method handles: ●Complex geometry ●Blunt or sharp notches ●Low notch-sensitive materials (e.g., grey cast iron) 5. Include Surface Effects If the camshaft is surface-hardened: ●Measure surface hardness ●Apply correction for improved fatigue strength This significantly increases prediction accuracy. 6. Life Estimation Once crack initiation is predicted, crack growth laws (Paris law) estimate remaining life until fracture. Why Crack Modelling Works Best for Camshafts Camshafts experience: ●High-cycle fatigue ●Multiaxial loading ●Stress concentrations ●Surface condition effects Crack modelling captures all of these, making it the most reliable method for modern camshaft fatigue design.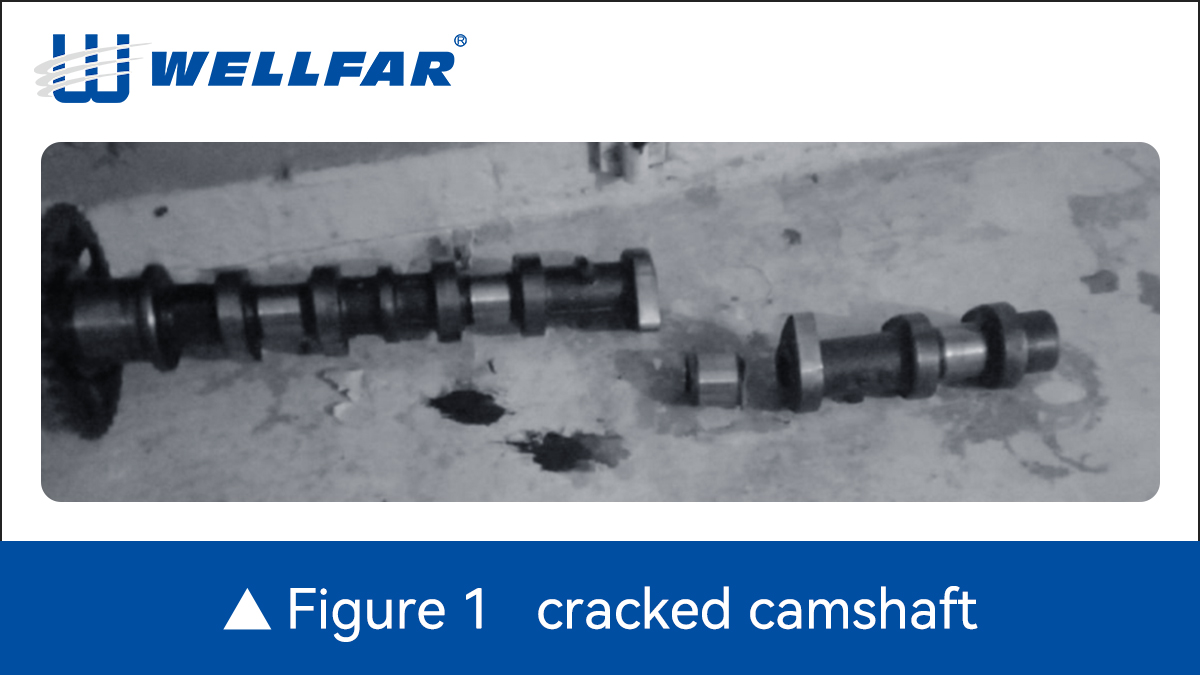
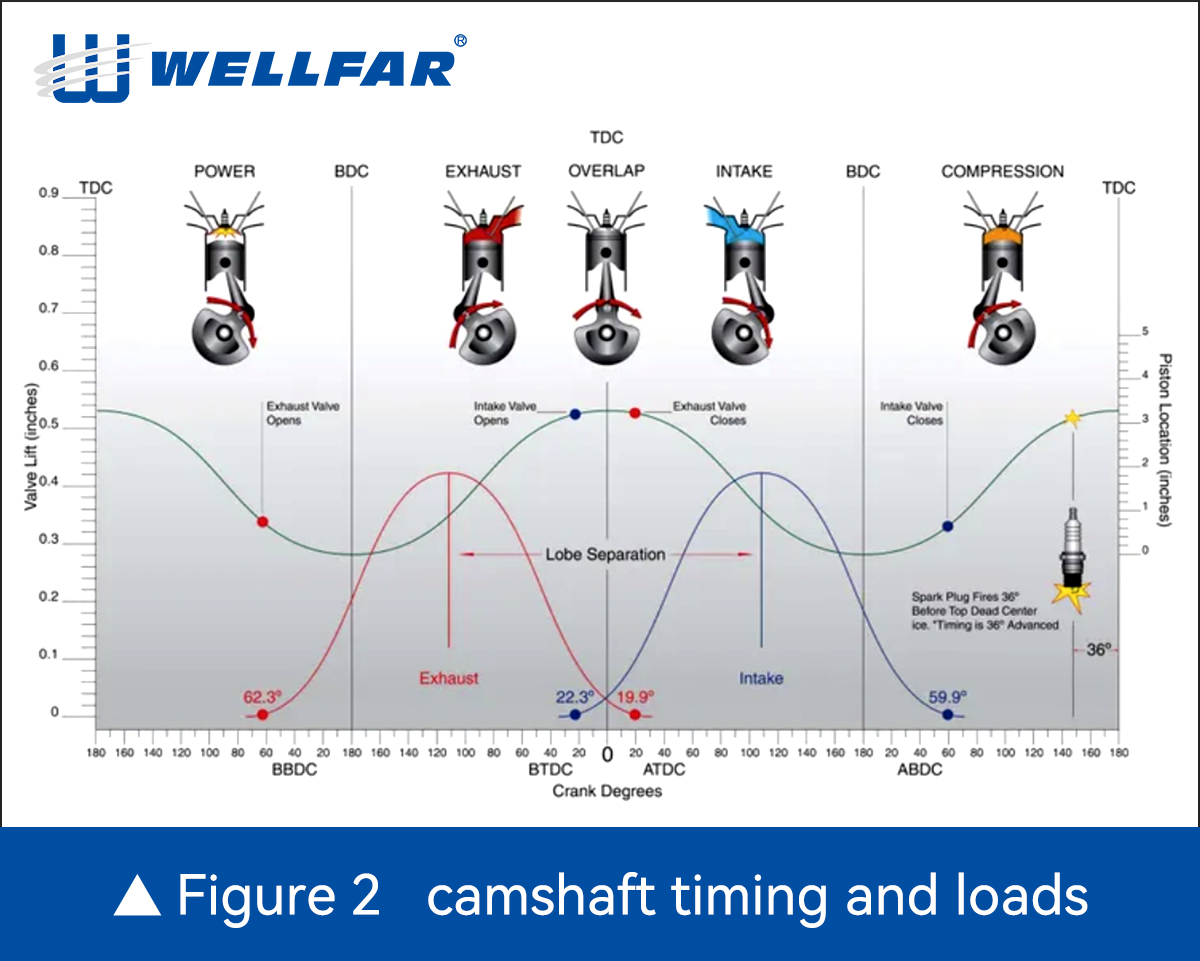
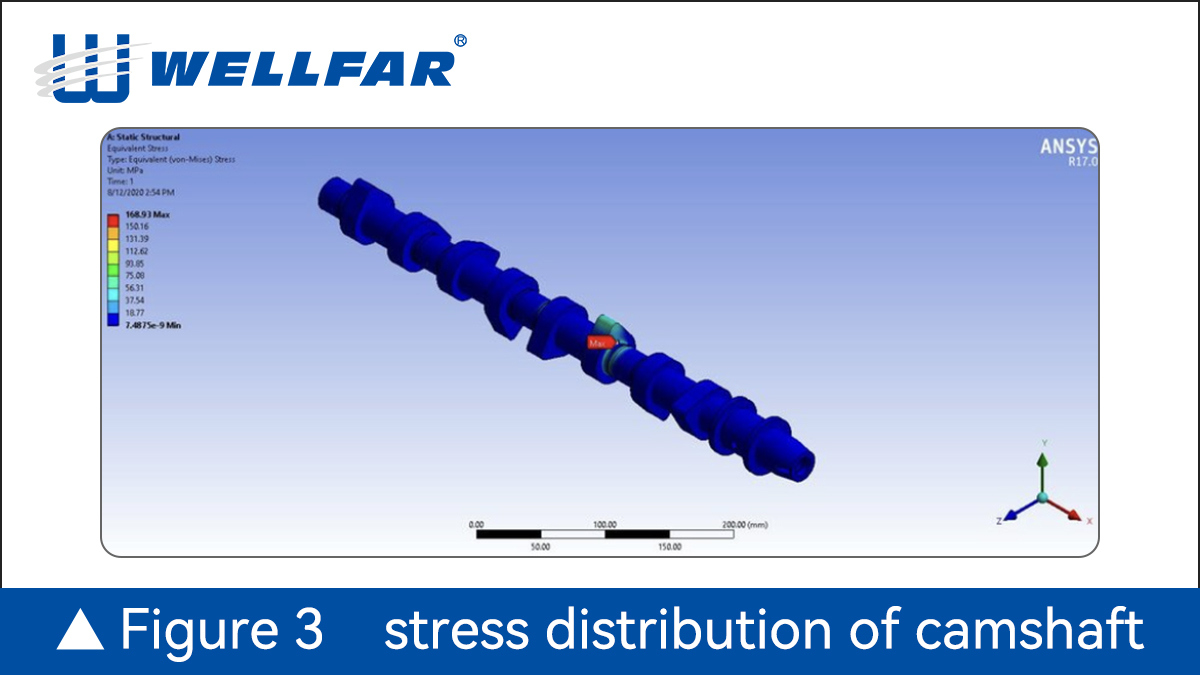
Fatigue Failure In A Camshaft Normally Starts At Stress Concentrations Such As Fillets
2026-02-06 00:26






